In the fast-paced digital world, where staying connected is crucial, the iPhone has become an indispensable companion for people from all walks of life. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just getting acquainted with your device, having a reliable WiFi connection is essential for seamless communication and accessing information on the go.
Hello, I’m Mannan Wasif, and I’m thrilled to be your dedicated iPhone expert, sharing valuable tips and tricks to enhance your iPhone experience. With years of expertise under my belt, I’m here to guide you on How to connect to 2.4 GHz WiFi on iPhone. So, let’s embark on this journey together and ensure you’re always connected to the right network.
When it comes to transmitting wireless internet connections, most routers rely on two distinct frequencies: the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Each has its own advantages and limitations, giving you the flexibility to choose according to your specific needs.
However, it’s essential to understand the differences between these bands to optimize your WiFi experience. The 2.4GHz band offers a broader coverage area but slightly slower data speeds, while the 5GHz band provides faster data transfer rates but over a more limited range.
Although your router typically handles connection selection, let’s explore how you can manually connect to a 2.4 GHz WiFi network on your iPhone.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to effortlessly identify and connect to a 2.4 GHz WiFi network. Whether you’re facing connectivity issues or simply want to take advantage of the 2.4 GHz band’s specific benefits, you’ve come to the right place.
Discovering and connecting to the correct network ensures a smoother experience for all your online activities, from browsing the web and streaming content to connecting with friends and family.
So, whether you’re a seasoned iPhone user or a newcomer to the Apple ecosystem, let’s dive into the world of 2.4 GHz WiFi on your iPhone and make sure you stay connected with ease.
Want to Enhance WiFi Privacy? Unlock the potential of your WiFi security. Dive into our guide on changing WiFi passwords on the iPhone.
How to find your 2.4 GHz WiFi network?
Make sure that when connecting your mobile device and Arlo device to a WiFi network, the SSID identifies it as a 2.4 GHz network. SSIDs typically end in 2, 2.4, or 2G.
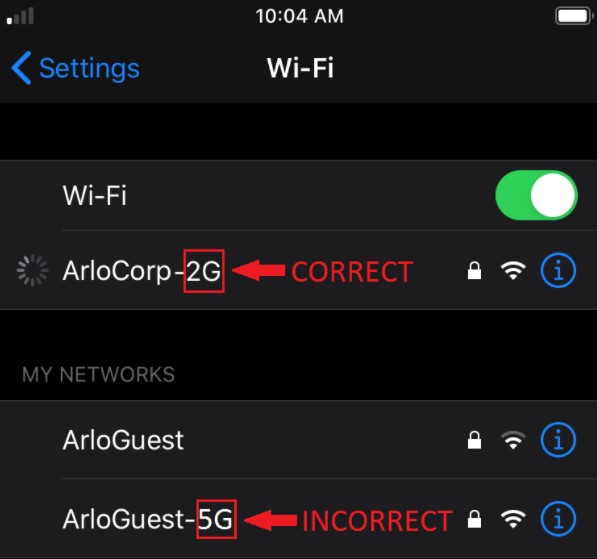
WiFi routers typically use a single network name for both their 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. If you’re having difficulty connecting and the name of your WiFi network doesn’t show whether it’s 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, please read the Troubleshooting section.
Troubleshooting
If your WiFi network name or SSID doesn’t indicate whether it’s 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz
- Check your router’s settings to see if you have a 2.4 GHz WiFi network that your mobile device can connect to. If you need assistance, contact your router manufacturer.
- Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can assist you in connecting your mobile device to a 2.4 GHz WiFi network.
If your router has the same SSID or network name for both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
- Both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi networks are broadcast using the same network name, or SSID, on mesh WiFi networks. If your mobile device is connected to a mesh network, your Arlo device is unable to connect to the 5 GHz band, so it will connect to the 2.4 GHz band.
How to connect to 2.4GHz wifi?
Navigate to the Settings menu and click on Wi-Fi to verify your mobile device is connected to a 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi network. This menu displays all the available networks in your area. Your network’s SSID must be denoted by either a 2G (2.4) or 5G (5.0) end. 5G refers to a frequency of 5 GHz, while 2G is in the 2.4 GHz band. Tap the SSID that has 2G or 2.4 for the end notation and enter the Wi-Fi password for the network you want to connect to.
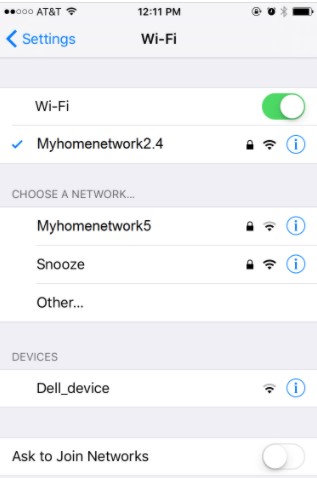
You will need to obtain this information from your router if you are having difficulties finding out if you are on a 2.4 GHz WiFi network. You may refer to the router manufacturer’s or user manual for more details on this process
Follow these steps to connect your iPhone to a 2.4 GHz network
Follow these steps to connect your iPhone to a 2.4 GHz network:
- The first step is to unlock your iPhone and go to the Applications menu.
Ready to Power Up? Learn how to turn on your iPhone 11 and get started with our step-by-step guide.
- To access Settings, tap the icon. The Settings section of your iPhone will open.
- In the Settings section, you must enable WiFi by tapping the switch or slider next to it (at the top).
- After enabling the WiFi option, you will be able to select a 2.4 GHz WiFi network from the list that appears. A 2.4 GHz WiFi network is typically identified by a 2, 2.4, or 2G at the end, also known as an SSID.
- Next, enter the password after selecting the WiFi network, which you will need to do in the appropriate field, and click Connect. You will be able to see a blue checkmark next to the name of the WiFi network once you have connected
I’ve written more guides within the “Connect” category. This section covers topics such as “How To Connect iPhone To MacBook,” “How To Connect Blue Yeti To iPhone,” and more. In order to improve your overall understanding of these subjects, I recommend dedicating additional time to studying them.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 2.4GHz WiFi
Certainly! Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of using 2.4 GHz WiFi:
Advantages
Here are some of the advantages of using 2.4 GHz WiFi:
- Wider Coverage Area: One of the primary advantages of the 2.4 GHz WiFi band is its ability to provide broader coverage. The lower frequency of 2.4 GHz allows the signal to penetrate walls and obstacles more effectively, making it ideal for larger homes or spaces with multiple rooms.
- Better Penetration through Obstructions: 2.4 GHz signals are better at passing through solid objects like walls and furniture. This characteristic makes it more reliable in environments with physical barriers, ensuring a more stable connection throughout the area.
- Compatible with Older Devices: Many older wireless devices, such as older smartphones, laptops, and IoT devices, support only the 2.4 GHz frequency. By using the 2.4 GHz band, you ensure compatibility with a wider range of devices, making it convenient for guests or older gadgets in your network.
- Interference Avoidance: The 2.4 GHz band has a longer wavelength compared to the 5 GHz band. As a result, it is less susceptible to interference from other electronic devices that operate on similar frequencies, such as microwaves and cordless phones.
- Longer Range Outdoors: In outdoor settings, where distance and obstacles play a significant role, the 2.4 GHz band often outperforms 5 GHz. This makes it well-suited for activities like gardening or relaxing on the patio while staying connected.
- Suitable for IoT Devices: Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as smart home appliances, cameras, and sensors, often rely on the 2.4 GHz band for connectivity. Using 2.4 GHz WiFi ensures seamless communication with these IoT devices and enhances your smart home experience.
Disadvantages
Here are some of the disadvantages of using 2.4 GHz WiFi:
- Slower Data Transfer Speeds: One of the significant drawbacks of the 2.4 GHz WiFi band is its limited data transfer speed compared to the 5 GHz band. Due to its lower frequency, it cannot support as much data throughput, resulting in slower download and upload speeds, especially in crowded WiFi environments.
- More Susceptible to Interference: The 2.4 GHz band operates on a frequency that is more commonly used by various household devices, such as cordless phones, baby monitors, and Bluetooth devices. This higher level of interference can cause signal disruptions and reduce the overall network’s performance.
- Crowded and Congested Channels: In urban or densely populated areas, the 2.4 GHz band can become overcrowded as numerous WiFi networks and devices compete for the limited number of available channels. This congestion leads to increased signal interference and reduced network efficiency.
- Limited Number of Non-Overlapping Channels: The 2.4 GHz band has only three non-overlapping channels (channels 1, 6, and 11 in the United States), which further exacerbates the issue of interference. With so few non-overlapping channels, it becomes challenging to find a clear channel for optimal network performance.
- Dual-Band Devices May Prefer 5GHz: Many modern devices are now dual-band, meaning they can connect to both 2.4GHz and 5GHz networks. In situations where both bands are available, these devices may prefer the 5 GHz band due to its higher data speeds, potentially leaving the 2.4 GHz band underutilized.
- Limited Support for High-Bandwidth Applications: Activities that require significant bandwidth, such as 4K video streaming and online gaming, may experience lags and buffering on a 2.4GHz network due to its slower data speeds.
- Range Versus Speed Trade-Off: While the 2.4GHz band offers a more extensive coverage area, this advantage comes at the expense of data speed. Users may need to compromise between coverage range and faster connection speeds when choosing the appropriate WiFi band.
How To Tell If iPhone Is Connected to 2.4 Or 5GHz WiFi?
Apple’s iPhone is its flagship phone and is considered to be the most advanced on the market. In spite of arguable features and opinions and an ongoing debate about whether Apple or Android is superior, the iPhone and iOS have more stability and a better user interface than any other option.
One of the best things about iOS is that it has premium features, and there are no lags whatsoever.
Here are a few things that you must know about the band that your iPhone is connected to with your router:
1. On your phone
In general, iPhone features don’t give you access to certain information due to the closed system, and Apple claims it’s the best thing for security and securing your personal data.
Therefore, if you are connected to a 5 GHz or 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi band, you will not be able to get the information on your iPhone. There is no doubt that the phone does not show this information, but there are some possibilities that might let you guess what frequency you are connected to.
2. Signal Strength
A good way to judge the frequency you are connected to is to look at the signal strength, but you will need to move away from the router to do this properly. Most people know that the 2.4 GHz band of Wi-Fi has a stronger signal and more power than the 5 GHz band. As a result, you will have to move away from the router and see which of the SSIDs has the strongest signal.
You can determine the 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi using the SSID with more bars and the 5 GHz Wi-Fi using the SSID with fewer bars or disappearing. But this is only a guess, and it might change.
3. Speed
It is also possible for you to perform a speed test to find out the Wi-Fi frequency band you are connected to. If you connect both SSIDs to the device one by one, you can do a speed test, and the SSID with the higher speed will be 5 GHz. But again, this is another guess, and it might not be as accurate at all times due to differences in network traffic and other reasons.
4. Change SSID
Changing the SSIDs on both frequency bands is the best way to resolve this issue properly. You can change the SSID on both frequencies of most of the routers, and that is going to help you solve the problem perfectly. By looking at the SSID, you can determine what frequency you’re connected to.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some Frequently Asked Questions about Connecting to 2.4 GHz WiFi on iPhone:
1. Why should I connect to a 2.4 GHz WiFi network on my iPhone?
Connecting to a 2.4 GHz WiFi network offers several advantages, including wider coverage, better penetration through obstacles, and compatibility with older devices. If you have a large home or want to ensure a stable connection in areas with walls or obstructions, the 2.4 GHz band can be a reliable choice.
2. Can I switch between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi on my iPhone?
Yes, if your router supports both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, your iPhone can switch between them automatically based on signal strength and device compatibility. However, you can manually connect to a specific frequency in the Wi-Fi settings if needed.
3. How can I avoid interference on my 2.4 GHz WiFi network?
To reduce interference, consider placing your router away from other electronic devices, such as microwaves and cordless phones. Additionally, using a less crowded WiFi channel (1, 6, or 11) and choosing the 5 GHz band for bandwidth-intensive tasks can help improve performance.
4. My iPhone automatically connects to 5 GHz. How can I connect to a 2.4 GHz network instead?
In the Wi-Fi settings, you can forget the 5 GHz network your iPhone is currently connected to. Then, refresh the Wi-Fi list and manually select the 2.4 GHz network you wish to connect to.
5. Is 2.4 GHz WiFi suitable for gaming and streaming on my iPhone?
While 2.4 GHz WiFi can handle basic internet tasks, it may not be ideal for demanding activities like online gaming or 4K streaming due to its slower speeds. For optimal performance in such scenarios, consider using the 5 GHz band if available.
6. Can I change my WiFi network’s frequency on my router?
Yes, many modern routers allow you to set separate network names (SSIDs) for the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Check your router’s settings or user manual to configure the frequencies independently.
7. Are there any security concerns specific to 2.4 GHz WiFi networks?
The security concerns for both 2.4GHz and 5GHz WiFi networks are generally similar. It is essential to use strong passwords, enable WPA/WPA2 encryption, and keep your router’s firmware updated to ensure network security.
8. How do I troubleshoot if I can’t find my 2.4GHz WiFi network on my iPhone?
If you can’t find your 2.4 GHz network, check your router’s settings to ensure it is broadcasting the 2.4 GHz frequency. Also, make sure your iPhone’s Wi-Fi is enabled, and consider restarting both your iPhone and router to refresh the connection. If the issue persists, contact your router manufacturer or Internet Service Provider for further assistance.
9. How do I check if my iPhone is connected to a 2.4 GHz WiFi network?
To check your connection, go to the Settings menu, tap on Wi-Fi, and verify that your iPhone is connected to an SSID with “2G,” “2.4,” or “2” at the end. This indicates that you are connected to a 2.4 GHz WiFi network.
10. Are there any disadvantages to using 2.4 GHz WiFi on my iPhone?
While 2.4 GHz WiFi has its benefits, it also comes with some drawbacks. These include slower data transfer speeds, susceptibility to interference from other devices, and limited non-overlapping channels, especially in densely populated areas.






